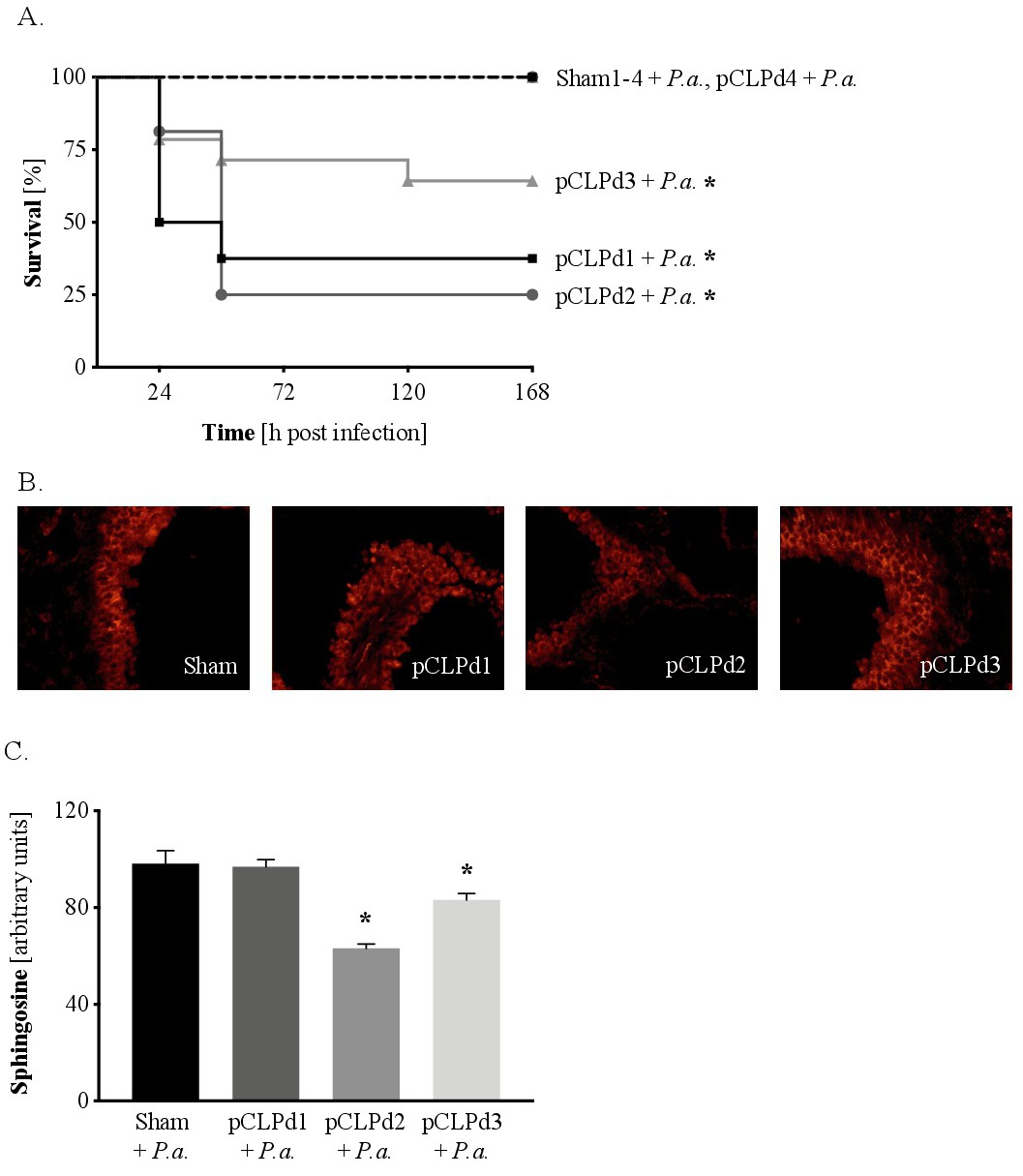
Fig. 2. Septic mice are susceptible to pulmonary P. aeruginosa infection up to three days after CLP and their airway sphingosine levels are reduced. (A) Mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and inoculated intranasally with 106 CFU P. aeruginosa 762 one, two, three or four days later. Survival was monitored for 7 days after infection. n = 16 mice/group (days 1 and 2), n = 14 mice/group (day 3), n = 8 mice/group (day 4) spread across two biologically independent experiments. * p<0.05 vs respective Sham + P.a. (log-rank test). (B+C) Mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). One, two or three days after sham or CLP surgery, in the absence of pulmonary infection, sphingosine levels in tracheal epithelial cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence (400x magnification). (B) A representative section is shown for each group. (C) The sphingosine signal in the respiratory epithelium was quantified using ImageJ. n = 3-4 mice/group and 15-20 vision fields/mouse were analyzed. * p<0.05 vs Sham (ANOVA with Dunnett posttest).